


Next: Optical bench
Up: Instrument layout
Previous: Instrument layout
The dark-speckle coronagraph (DSC) combines features of adaptive optics, Lyot
coronagraphy and speckle interferometry.
Figure 1 shows the arrangement utilized at the Coudé focus of the 152cm telescope
at
Observatoire de Haute-Provence.
The stellar beam from the telescope enters the adaptive optics bench BOA, of the
ONERA
(Office National d'Etudes et de Recherches Aérospatiales). It has 88
actuators and responds fast enough for seeing correction in the visible range
([Conan et al. 1998]).
Downstream from BOA, the afocal beam reaches a dichroic beamsplitter
which transmits the IR (K band) light towards another instrument used
simultaneously, the achromatic interfero-coronagraph ([Gay & Rabbia 1996]), while
visible
light (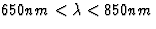 ) is reflected to the DSC.
) is reflected to the DSC.
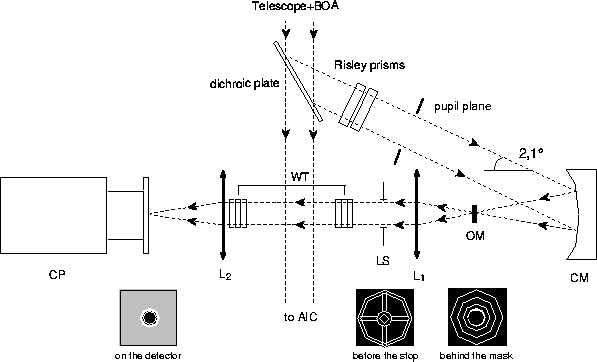
Figure:
Dark speckle camera used at the Haute-Provence 1.52m telescope (not
a scale drawing). The dichroic beam-splitter selects the wavelength range
650-850nm in reflection. The collimated beam received from the telescope with
BOA adaptive optics crosses a pair of Risley prisms for atmospheric dispersion
compensation and is focussed by concave
mirror CM onto the Lyot occulting mask OM. The masked field is re-imaged onto
photon-counting camera CP through the pair of Wynne corrector triplets WT
which compensate the first-order lateral chromatism of diffraction patterns.
A Lyot stop LS removes stellar diffracted light at the edge of the
relayed pupil, according to the classical Lyot coronagraph principle.
 |
The Strehl ratio reached 10% to 30% depending on seeing conditions. Although
the adaptive optics gain is higher in the IR range, the advantage of working
with visible light results from the use of a photon-counting camera.
Its low dark count allows short exposures with negligible added noise, as
required for speckle observations.
The centering of the star's image on the Lyot occulting mask is critical,
and should be part of the adaptive optics loop. This is achievable by
collecting light reflected from the mask, but the drift had to be corrected
manually at this stage.



Next: Optical bench
Up: Instrument layout
Previous: Instrument layout
6/15/1998

